Exploring Effective Treatments for Eczema: A Path to Relief
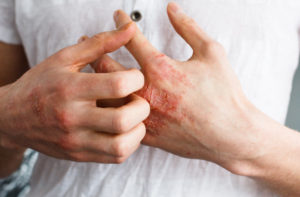
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to itchy, inflamed, and often painful skin. While there is currently no cure for eczema, understanding and utilizing the right treatments for eczema can significantly reduce symptoms, improve skin health, and enhance the quality of life for those affected. This comprehensive guide delves into the various treatments for eczema, offering insights into how individuals can find relief and manage their condition effectively.
Understanding Eczema and Its Impact
Eczema is characterized by dry, itchy skin that can become red, inflamed, and vulnerable to infections. It can appear anywhere on the body and is known for its fluctuating severity, with periods of flare-ups followed by times of remission. The condition not only affects physical health but can also impact emotional wellbeing, making effective treatment strategies crucial for those affected.
Key Treatments for Eczema
Managing eczema involves a multifaceted approach that includes skincare routines, medication, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes, professional medical treatments. Here’s a closer look at the main treatments for eczema:
1. Moisturizing
Regular use of moisturizers is fundamental in managing eczema. Moisturizers help to repair the skin barrier, reduce dryness, and alleviate itching. For best results, choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products designed for sensitive skin, and apply them several times a day, especially after bathing.
2. Topical Medications
Corticosteroids: These are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching. They come in various strengths and should be used as directed by a healthcare provider to avoid potential side effects.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: These non-steroidal creams or ointments, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, reduce inflammation and can be used on sensitive areas where steroids are unsuitable.
3. Systemic Treatments
For severe eczema cases that don’t respond to topical treatments, doctors may prescribe systemic medications. These can include oral drugs that suppress the immune system or biologic drugs designed to target a specific part of the immune system involved in inflammation.
4. Light Therapy
Phototherapy or light therapy involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial UV light. It’s beneficial for reducing symptoms and inflammation in some people with moderate to severe eczema.
5. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding irritants and allergens that trigger eczema flare-ups can be a helpful strategy.
Stress Management: Since stress can exacerbate eczema, techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular exercise can be beneficial.
Wet Wraps: Applying wet wraps to moisturized skin can help soothe and hydrate severely affected areas.
6. Dietary Changes
While not directly a treatment, some individuals find that certain foods can trigger their eczema. Working with a healthcare provider to identify and eliminate potential food allergens may provide relief for some.
The Importance of a Tailored Approach
Because eczema can vary significantly from person to person, what works for one individual may not work for another. Collaborating with a dermatologist or healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan to your specific needs is crucial. This personalized approach ensures that treatments for eczema are as effective as possible, taking into account the severity of the condition, personal health history, and lifestyle factors.
Conclusion
Living with eczema can be challenging, but with the right treatments and strategies, individuals can achieve significant relief from symptoms and improve their quality of life. From daily skincare routines and medications to lifestyle adjustments and professional treatments, there are numerous avenues to explore in the management of eczema. It’s important to remember that managing eczema is an ongoing process, and working closely with healthcare professionals to adjust treatments as needed is key to finding long-term relief.